There is no easy answer to this question. Every family is different; as is every circumstance. The best guidance we can offer is to take your time and do your homework before borrowing any loan.
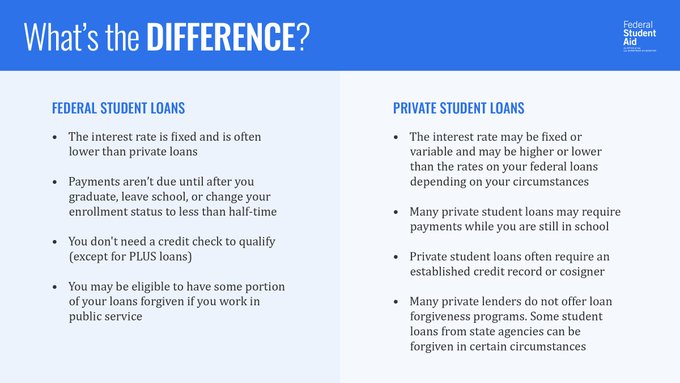
Federal student loans are made by the government, with terms and conditions that are set by law, and include many benefits (such as fixed interest rates and income-driven repayment plans) not typically offered with private loans.
Federal student loans offer many benefits compared to other options you may consider when paying for college:
-
The interest rate on federal student loans is fixed and usually lower than that on private loans—and much lower than that on a credit card.
-
You don’t need a credit check or a cosigner to get most federal student loans, unless it is a Direct PLUS Loan. Direct PLUS Loans require a credit check to be completed by the U.S. Department of Education.
-
You must not have an adverse credit history. If you have an adverse credit history, you may still be able to receive a PLUS loan if you meet additional requirements.
-
-
You don’t have to begin repaying your federal student loans until after you leave college or drop below half-time.
-
If you demonstrate financial need, the government pays the interest on some loan types while you are in school and during some periods after school.
-
Federal student loans offer flexible repayment plans and options to temporarily postpone your loan payments if you’re having trouble making payments.
-
If you work in certain jobs, you may be eligible to have a portion of your federal student loans forgiven if you meet certain conditions.
In contrast, private loans are made by private organizations such as banks, credit unions, and state-based or state-affiliated organizations, and have terms and conditions that are set by the lender. Private student loans are generally more expensive than federal student loans.
When researching private loans keep in mind:
- Interest rates for private loans are higher than those for federal student loans. Lenders can offer fixed or variable interest rates. You will need to contact the lender for more information.
- Private lenders may charge additional loan fees such as origination fees, monthly service charges, or late fees.
- Private lenders are subject to credit approval and will complete a credit check when you apply. Lenders may require a good credit score and a co-signer.
- Private lenders may not offer repayment plans as flexible or varied as those for federal loans. You will need to contact your lender for specific details for repayment.
- A private loan can only be certified up to your remaining unmet cost of attendance.
- Cost of Attendance - Financial Aid Received = Unmet Cost of Attendance
- Compare private loans with different terms and interest rates with a private loan comparison calculator.
- Private loans differ by lender and by type of loan. Be sure you understand the terms of your loan, and keep in touch with your lender about any questions you may have.
For more detailed information on federal loans vs private loans please visit studentaid.gov or review the attachments for information on federal loans.